If cos 1 ( x 2 – y 2 / x 2 y 2) = tan 1 a , prove that dy/dx = y/x If cos 1 ( x 2 – y 2 / x 2I'm at the beggining of a differential equations course, and I'm stuck solving this equation $$(x^2y^2)dx2xy\ dy=0$$ I'm asked to solve it using 2 different methods I proved I can find integrating factors of type $\mu_1(x)$ and $\mu_2(y/x)$If I'm not wrong, these two integrating factors are $$\mu_1(x)=x^{2} \ \ , \ \ \mu_2(y/x)=\left(1\frac{y^2}{x^2}\right)^{2}$$ Then, I've used $\muThe general solution of y^2dx (x^2 – xy y^2)dy = 0 is (A) tan^1(x/y) logy c = 0

If Log Xy X 2 Y 2 Then Prove That Dy Dx Y 2x 2 1 X 1 2y 2 Brainly In
(x-2)dy/dx=y+2(x-2)^3
(x-2)dy/dx=y+2(x-2)^3-Jul 18, 16 · Solid Mensuration Prismatoid Differential Equation (1xy)^2 dx y^2 x^2 (1xy)^2 dy = 0 Differential Equation y' = x^3 2xy, where y (1)=1 and y' = 2 (2xy) that passes through (0,1) Tapered Beam Vickers hardness Distance between indentations Time rates Question for Problem #12 Make the curve y=ax³bx²cxd have a criticalDy/dx=x^22xyy^3=3x^2y 1 Ver respuesta tata25 está esperando tu ayuda Añade tu respuesta y gana puntos agustin agustin Respuesta que es eso no se lo que esta ai Nuevas preguntas de Matemáticas
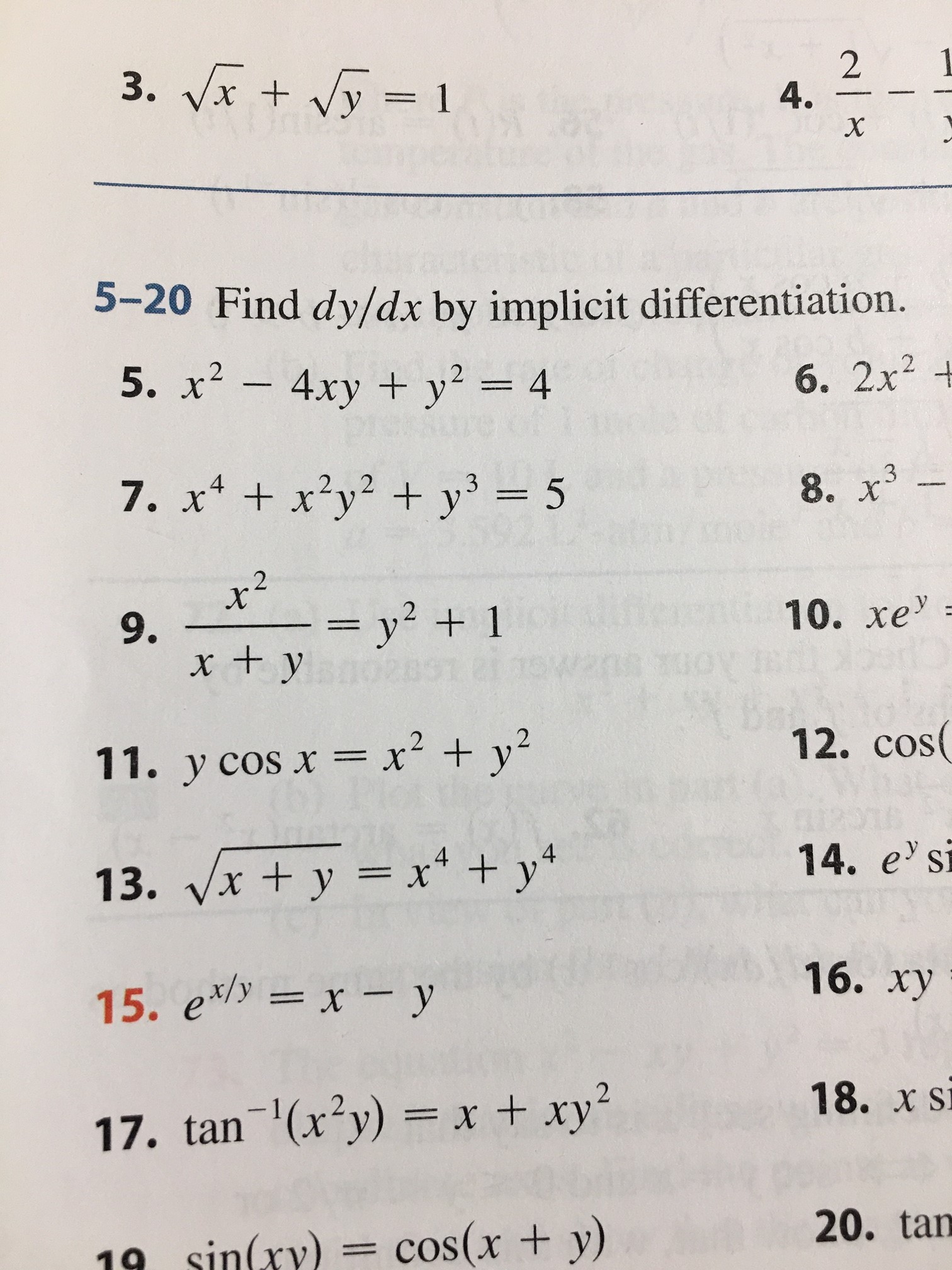


Answered 3 Vxy1 2 4 5 Find Dy Dx By Bartleby
Assuming that you've written this correctly, it is a differential equation so mathdy/dx = yy^2/math math1/(yy^2) dy = dx/math math1/(y*(1y)) dy = dx/math Let's break itGet an answer for '`tan^1(x^2 y) = x xy^2` Find `(dy/dx)` by implicit differentiation' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesCombine y^ {2}dx^ {2} and x^ {2}dy^ {2} to get 2y^ {2}dx^ {2} Combine y 2 d x 2 and x 2 d y 2 to get 2 y 2 d x 2 Combine all terms containing d Combine all terms containing d The equation is in standard form The equation is in standard form Divide 0 by 2y^ {2}x^ {2}x^ {2}y^ {2}
The derivative of the function `y = log(x 1/x)` with respect to x, `dy/dx` has to be determined It is assumed that log in the problem refers to natural logarithmClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Solve (x^2 y^2)dx xydy = 0Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music
D/dx x^2 y^4, d/dy x^2 y^4 Extended Keyboard;Answer to Solve the initial value problem dy/dx = (y^2 1)/(x^2 1), y(2) = 2 By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions toSwap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side dy=x^ {2}\frac {\mathrm {d} (y)} {\mathrm {d}x}xy\frac {\mathrm {d} (y)} {\mathrm {d}x} d y = − x 2 d x d ( y) x y d x d ( y) The equation is in standard form The equation is in standard form yd=0


Differential Equations Separation Of Variables Ppt Download



X Y 1 Dx Y X 1 Dy 0find The General Solution Of The Differential Equation Brainly In
See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Previous question Next question Transcribed Image Text from this Question Solve dy/dx = x^2 xy y^2/x^2 Get more help from Chegg Solve it with our calculus problem solver and calculatorQuestion Solve Dy/dx = X^2 Xy Y^2/x^2 This problem has been solved!If 2x2 3xy y2 x 2y 8 = 0, then dy/dx is equal to If 3 2 Cos Theta I Sin Theta A Ib Then A 2 2 B 2 Is If 3 Plus 3 Alpha Plus 3 Alpha Sq Infinity Eq 45 8 Then The Value Of Alpha Will Be If 3 Sin Theta 5 Cos Theta 5 Then 5 Sin Theta 3 Cos Theta Is If 3pi 4 Alpha Pi Then Root Cosec Square Alpha Plus 2 Cot Alpha


Solved Find The General Solution For The Following Differential Equation A Dy Dx Y E X B Cos Xdy Dx Y Sin X 1 5 Solve Dy Dx 1 Xy Xy 2 Course Hero



Solve Cos X Dy Y Sin X Y Dx Mathematics Stack Exchange
Jun 18, 07 · I'm improvingjust not quite there on these Find the particular solution of the given differential equation the condtion of y=3 when x=2 dy/dx = x/y^2 y^2 d/dy = x d/dx integral y^2 d/dy = integral x d/dx =1/3y^3 C = l/2 x^2 C y^3 = 3/2x^2 3Csub3 The book gives the answer of yTo find the solution of differential equation, Rewrite the given equation as, x2dy(y2−xy)dx= 0 x2dy = −(y2−xy)dx dy dx = (xy−y2) x2 x 2 d y ( y 2 − x y) d x = 0 x 2 d y = − ( y 2Mar 23, 18 · y(x)=2/(x^2C) Let's separate our variables, IE, have each side of the equation only in terms of one variable This entails dy/y^2=xdx Integrate each side intdy/y^2=intxdx 1/y=1/2x^2C Note that we would technically have constants of integration on both sides, but we moved them all over to the right and absorbed them into C



Solve Dy Dx 2xy X2 Y2 The Answer Given In The Book Is Y C X2 Y2 Brainly In


X 1 Y 2 Dx Y 1 X 2 Dy 0 Youtube
Jun 13, 11 · Favorite Answer X^2 dy/dxy^2=xy divide by x^2 dy/dx y^2 /x^2 = y/x dy/dx y/x = y^2 /x^2 divide both sides by y^2 y^ (2) dy/dx y^ (1) / x = x^ (2) (1) Let y^ (1) = v (1) y^ (2) dy/dx = dv/dx(d*y)/(d*x)(6*x^2*y^2)=0 Step by step solution Step 1 Equation at the end of step 1 dy —— ((2•3x 2) • y 2) = 0 dx Step 2 dy Simplify —— dx Canceling Out 21 Canceling out d as it appears on both sides of the fraction line Equation at the end of step 2 y — (2•3y 2 x 2) = 0 xSimple and best practice solution for (X^2y^2)dy=xy*dx equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework


How To Solve 2x Y 1 Dx X 4y 3 Dy 0 Quora



Engineering Mathematics Notes
Nov 17, 18 · 1answer Show that the differential equation (xy)dy/dx=x2y,is homogeneous and solve it askedApr 30, 18in Mathematicsby Nisa(596kpoints) differential equations class12 0votes 1answer (i) Prove that the DE is (3xy y^2) dx (x^2 xy) dyFind dy/dx given x^3 3 x^2 y 2 x y^2 = 12 Extended Keyboard;Calculus Applications of Definite Integrals Solving Separable Differential Equations 1 Answer Eddie Jul 11, 16 # y = xtan (ln x C)# Explanation This is a first order linear homogeneous equation NB



Ex 9 5 5 Show Homogeneous X2 Dy Dx X2 2y2 Xy Ex 9 5
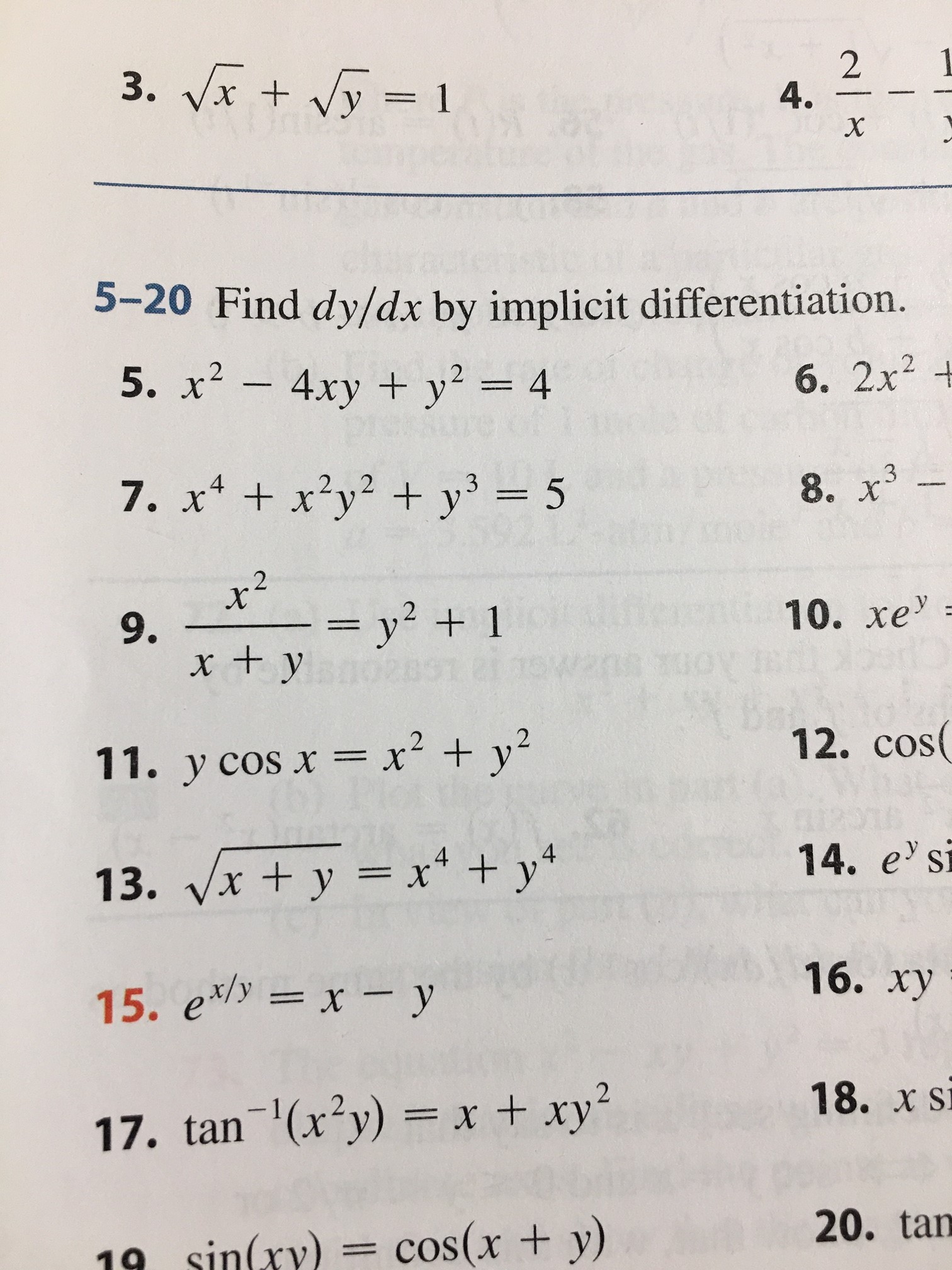


Answered 3 Vxy1 2 4 5 Find Dy Dx By Bartleby
Jul 11, 16 · What is a solution to the differential equation #dy/dx=y^2/x^2y/x1#?May 29, 18 · Ex 95, 4 show that the given differential equation is homogeneous and solve each of them (𝑥^2−𝑦^2 )𝑑𝑥2𝑥𝑦 𝑑𝑦=0 Step 1 Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 (𝑥^2−𝑦^2 )𝑑𝑥2𝑥𝑦 𝑑𝑦=0 2xy dy = − (𝑥^2−𝑦^2 ) dx 2xy dy = (𝑦^2−𝑥^2 ) dx 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑦^2 − 𝑥^2)/2𝑥𝑦 Step 2 Putting F(x, y) = 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 and finding FA first order Differential Equation is Homogeneous when it can be in this form dy dx = F ( y x ) We can solve it using Separation of Variables but first we create a new variable v = y x v = y x which is also y = vx And dy dx = d (vx) dx = v dx dx x dv dx (by the Product Rule) Which can be simplified to dy dx = v x dv dx



Example 21 Find General Solution Ydx X 2y2 Dy 0
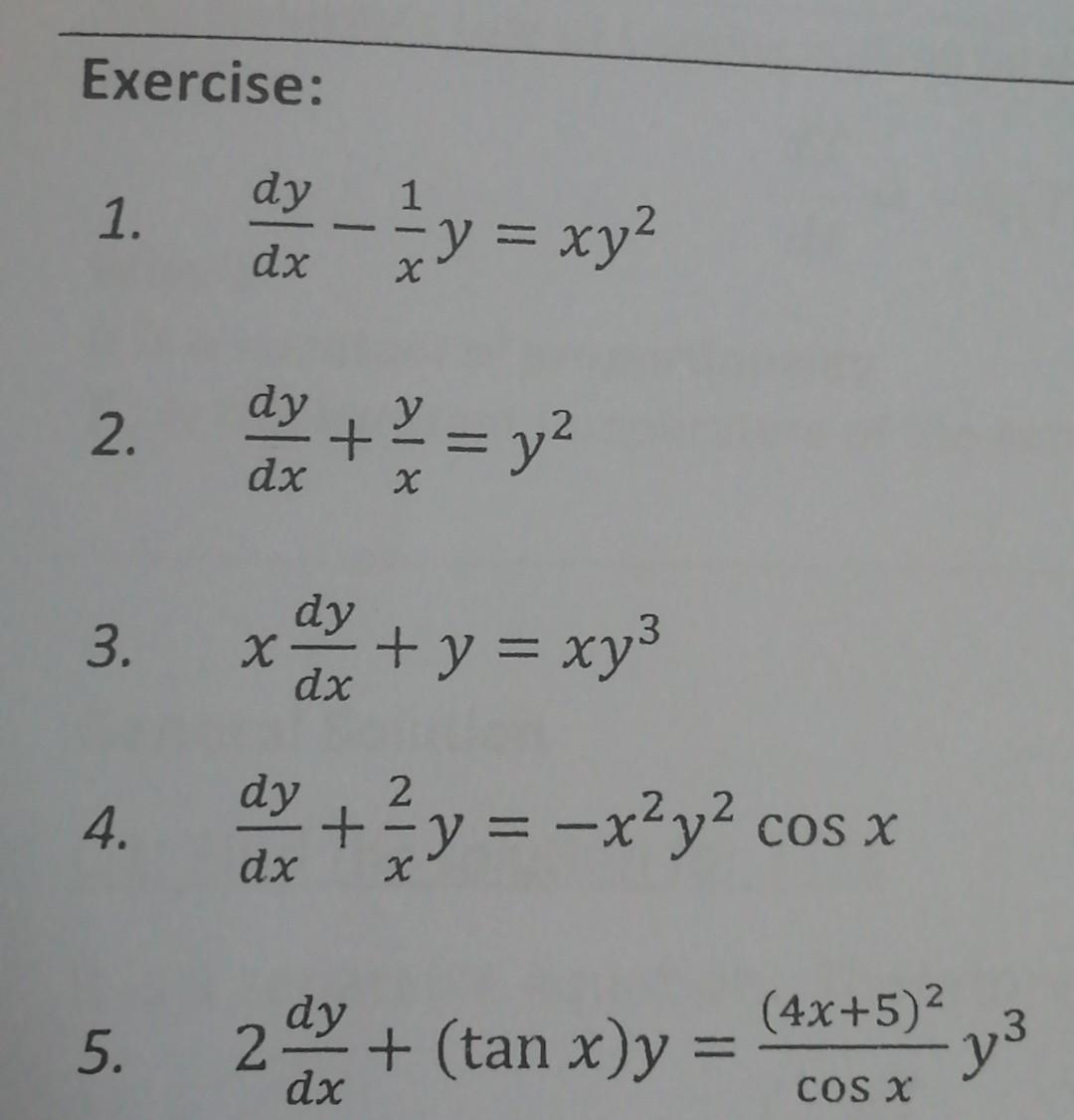


Solved Exercise 1 1 Dy Dx Y Xy2 H 2 Day Y2 3 Chegg Com
4 hours ago · I found the following problem in a textbook (translated) Evaluate $$\int_\gamma \frac{y}{x^2y^2}dx \frac{x}{x^2y^2}dy \ln{(z^4z^21)}dz$$ where $\;\gamma\;$ is given by the intersection bCalculus Find dy/dx y^2= (x1)/ (x1) y2 = x − 1 x 1 y 2 = x 1 x 1 Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y2) = d dx ( x−1 x1) d d x ( y 2) = d d x ( x 1 x 1) Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more steps2 4 dy x dx y a x 2b y 4c 11 m 15 1 9 m 15d 2 2 dyy x dx yx a 24 2 4 b from MTH 12 at University of Maryland, University College
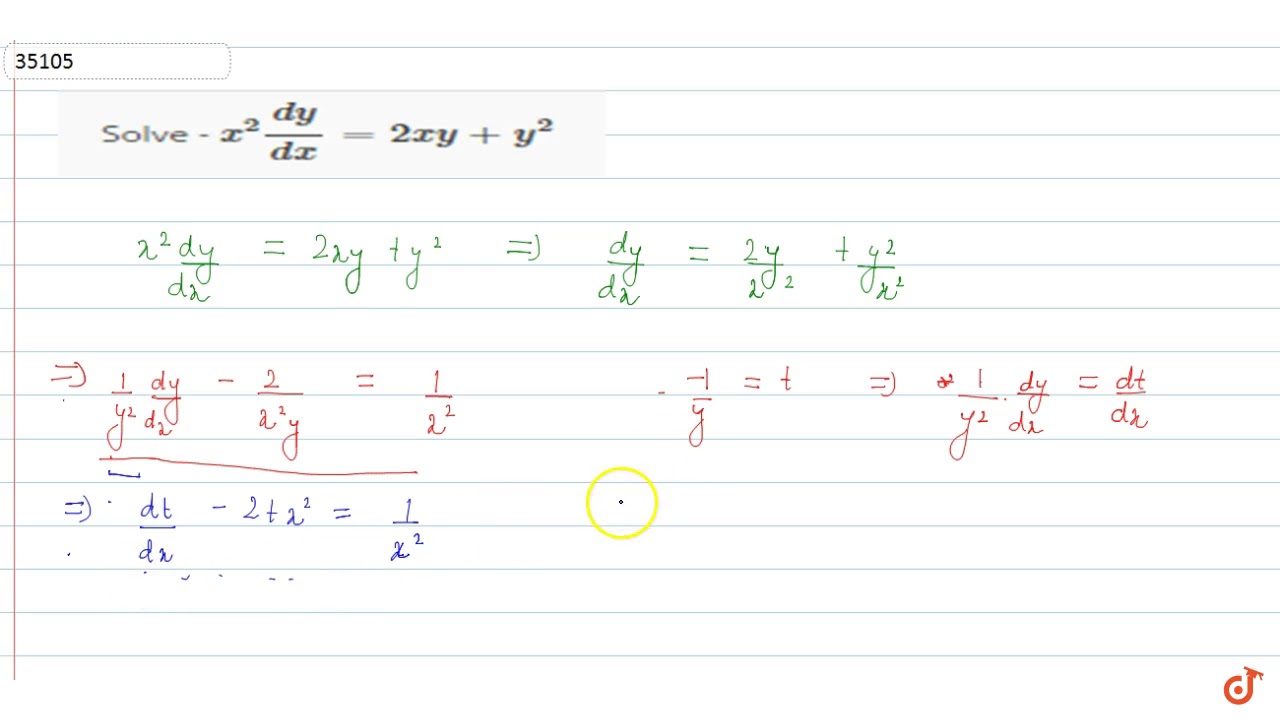


Solve X 2dy Dx 2xy Y 2 Youtube



Solution Solve The Linear Equation Dy Dx Y X X 2
Find dy/dx y=x^22 Differentiate both sides of the equation The derivative of with respect to is Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps By the Sum Rule, the derivative of with respect to is Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that is whereMay 29, 18 · Ex 94, 16 For xy dy/dx = (x 2) (y 2), find solution Chapter 9 Class 12 Differential Equations Serial order wiseJan 04, 13 · I found this initial value problem and was supposed to comment on the accuracy of Runge Kutta method Please enlighten me on the analytic solution Find y(2) given the differential equation \\frac{dy}{dx}=y^{2}x^{2} and the initial value y(1)=0 Thank you



Engineering Mathematics Notes



Engineering Mathematics Notes
If y = tan1 a/x log (xa/xa) 1/2, prove that dy/dx = 2a 3 /(x 4 – a 4) Mention each and every step Queries asked on Sunday & after 7pm from Monday to Saturday will be answered after 12pm the next working dayIf dy/dx = tan x, then y = А 2 12 tan x C B sec2xC C In secx C D In cosx C E sec x tanx C Get more help from Chegg Solve it with our calculus problem solver and calculatorAnswer The given equation can be written as dxdy = 3xy(x2 y2) (1) Put y = vx ⇒ dxdy



Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf Free Download
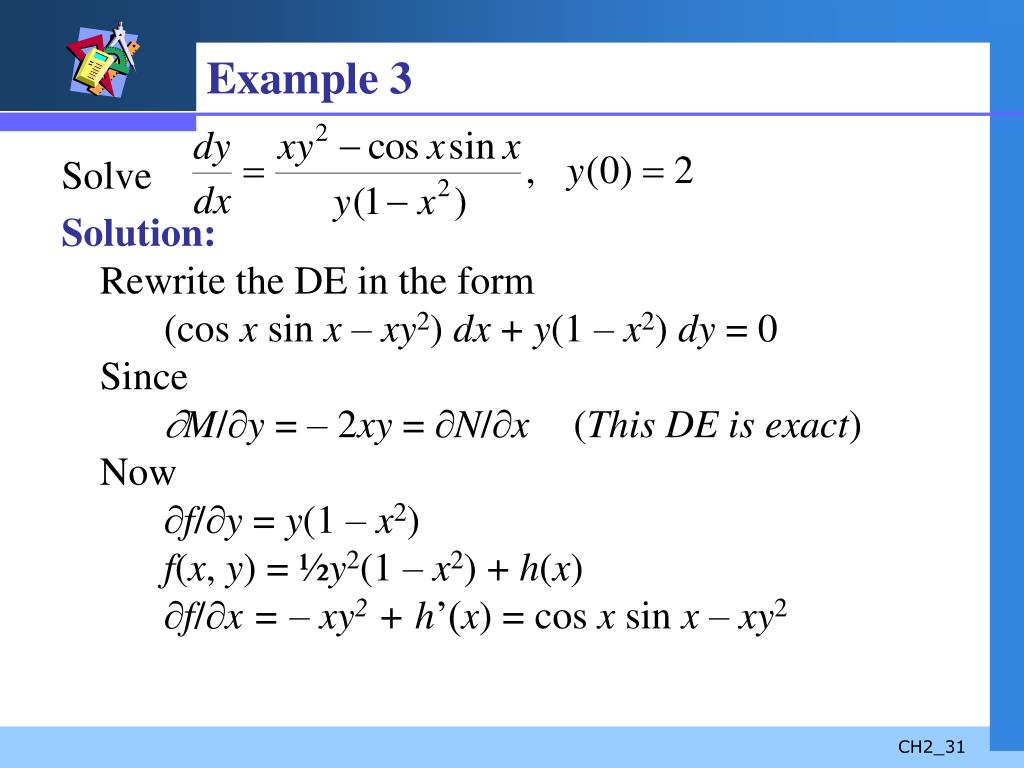


Ppt First Order Differential Equations Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
JEE Main 19 The solution of the differential equation , (dy/dx) = (xy)2 , when y(1) = 1, is (A) loge (2y/2x) = 2 (y1) (B) loge (2x/2Simple and best practice solution for (1x^2y^2x^2y^2)dy=y^2dx equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve itSep 10, 17 · 1/f df/dx = dy/dx ln2, df/dx = f ln 2 dy/dx= 2ŷ ln 2 dy/dx Put all to gether derivative is ln2 2^x ln 2 2^y dy/dx =ln2 2^x dy/dx dy/dx ( 12^y ln 2)=0 Since bracket can not be 0, dy/dx=0 Show more iceman Lv 7



If Y X 1 X Show That X 2 Dy Dx Xy 2 0



Hw 2 Fgh Criminology Crm512 Ufh Studocu
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, musicOct 18, 09 · Favorite Answer x dy/dx = sqrt (x^2 y^2) y (1) let y/x = v y = vx dy/dx = v x dv/dx substitute in eqn (1) x v x dv/dx = sqrt (x^2 v^2 x^2) vx vx x^2 dv/dx = x sqrt (1 v^2) vx x^2 dv/dx = x sqrt (1 v^2)Homogeneous Differential Equation (y^2 yx)dx x^2dy = 0If you enjoyed this video please consider liking, sharing, and subscribingYou can also help suppor



Solve Y 2 2x 2y Dx 2x 3 Xy Dy 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Solved The Given Differential Equations Are Linear Or Non Chegg Com
Solve the Differential Equation dy/dx=xy^2 In this tutorial we shall evaluate the simple differential equation of the form d y d x = x y 2 by using the method of separating the variables The differential equation of the form is given as d y d x = x y 2 Separating the variables, the given differential equation can be written asMay 23, · Solution for Solve dy/dx=2xy/(x^2y^2) Q A group of 150 tourists planned to visit East Africa Among them, 3 fall ill and did not come, of thIf x3 y3 3axy = 0, then dy/dx equals If xy = yx, then dy/dx = If Xe Xy Y Sin 2 X Then At X 0 Dy Dx If Xy And Z Are Nonzero Real Numbers And Axi2j Byj3k And Cxiyjzk Are Such That A X B Zi 3jk If Xyz0 Xyz2 Where Theta Is The Angle Between Y And Z Then The Value Of 2cosec2theta3cot2theta Is



If Xy 4 Prove That X Dy Dx Y 2 3y Brainly In
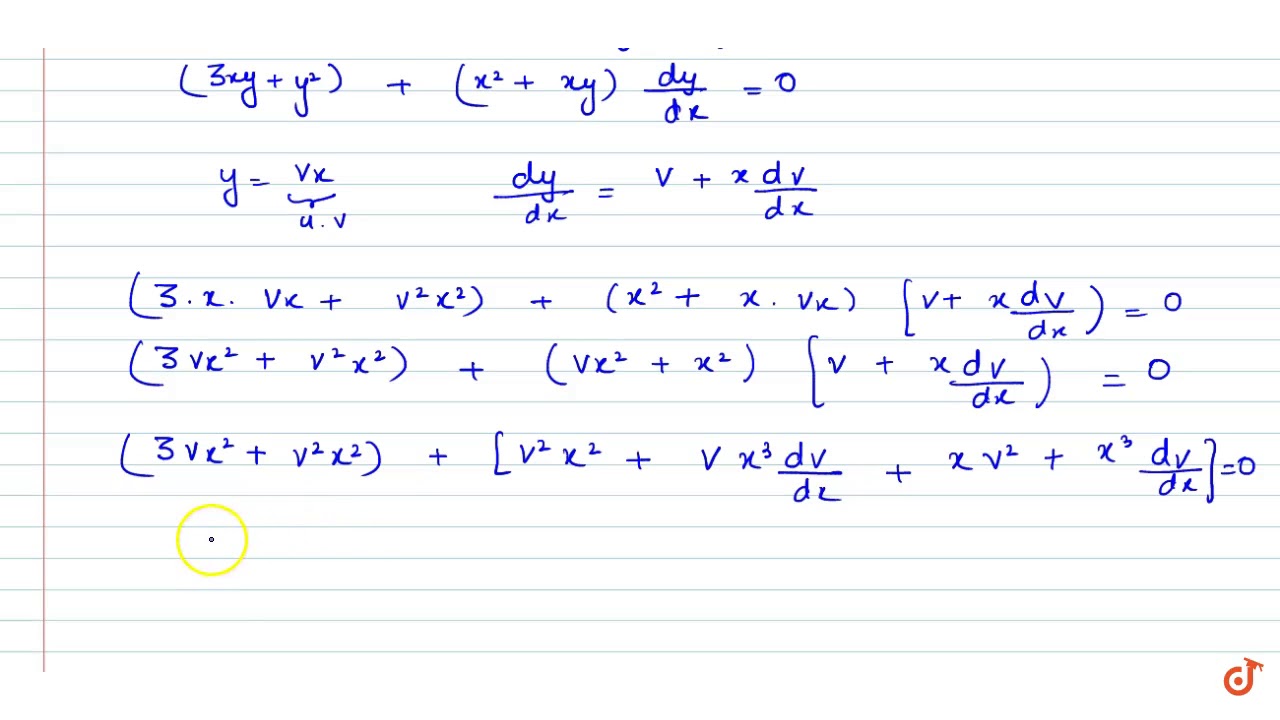


3x Y Y 2 Dx X 2 X Y Dy 0 Youtube
Free ordinary differential equations (ODE) calculator solve ordinary differential equations (ODE) stepbystepMar 31, 18 · Solve the differential equation dy = cos x (2y cosec x) dx given that y = 2 when x = π/2 asked Mar 31, 18 in Class XII Maths by nikita74 (1,017 points)Free separable differential equations calculator solve separable differential equations stepbystep


Differential Equations Separation Of Variables Ppt Download



Engineering Mathematics Notes
X 2 d y d x = y − x y = y (1 − x) Next, we want to separate the variables, ie we want all the 'y' terms on the left side and all the 'x' terms of the right side To do this, let's first divide both sides of the equation by y x 2, giving us 1 y d y d x = 1 − x x 2 = x − 2 − x − 1 To move the 'dx' across, we integrate both sides with respect to xQ If y = 2^x, find dy/dx 3) Differentiate both sides with respect to x LHS log (y) => (1/y) (dy/dx) partial differentiation hence we multiply (1/y) by dy/dx 4) We want to find dy/dx, which is on the LHS To get this dy/dx on its own we can multiply both sides by y 5) To finish this question we need to sub in for y and then we have an



Engineering Mathematics Notes
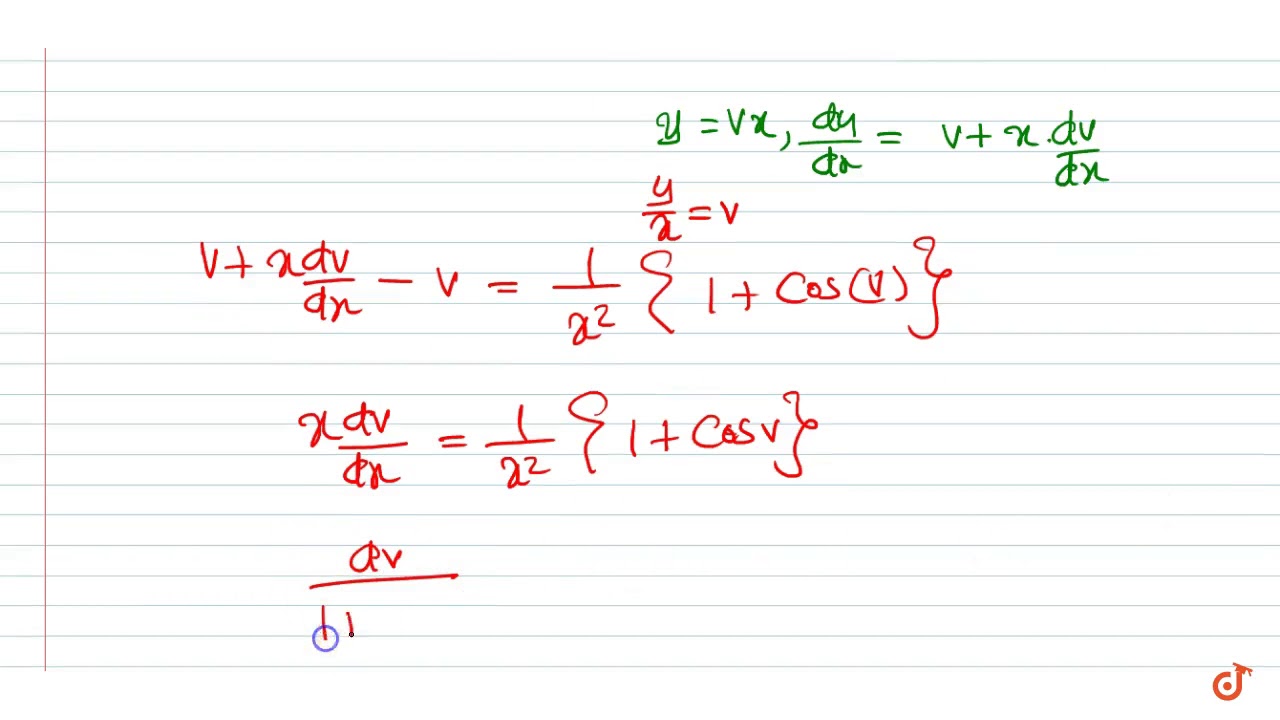


Solve The Following Differential Equation X 2 Dy Dx Xy 1 Cos Y X X 0 Youtube



Math 432 Hw 2 4 Solutions



Solve 3xy 2ay 2 Dx X 2 2axy Dy 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Consider The Differential Equation Dy Dx Y 3 2 X Y 2 X 2



The Solution Of The Differential Equation Y Xy 2x 2y 2 Dx X Xy X 2y 2 Dy 0 Is Given Youtube


Bernoulli Differential Equation Dy Dx Y Xy 2 1 Youtube



Solve X 3 2y 3 Dx 3xy 2dy 0



Solution 1 Xsqrt X 2 Y 2 Dx Y 1 Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Dy 0 Is X Y


How Do You Solve Dy Dx Y 2xsqrt 1 X 2 Where Y 1 When X 0 Socratic



Solve The Following Differential Equation Xy Dy Dx Y 2 X Y



Solve Y 1 Xy Dx X 1 Xy X 2y 2 Dy 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Solve The Following Equation Dydx Xy Y 2e X 2 2 Sin X



Ex 9 6 3 Find General Solution Dy Dx Y X X2 Ex 9 6



Differential Equation X Dy Dx Y Xy2 Brainly In



If Log Xy X 2 Y 2 Then Prove That Dy Dx Y 2x 2 1 X 1 2y 2 Brainly In



Solve X 2 D 2y Dx 2 2x Dy Dx 4y X 2 2log X Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection



Solve Y 2 2x 2y Dx 2x 3 Xy Dy 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



For What Value Of N Is Following A Homogeneous Differential Equation



Solve The Following Different Al Exercise Begin Array Ll Text I Y 2 D X Left X Y X 2 Right D Y 0 Text Exercise Text Ii X 2 Y D X Left X 3 Y 3 Right D Y 0



Tutorial 4 Question For Solution By Substitutions Studocu



Y 2 X 2 Dy Dx Xy Dy Dx Youtube



How To Solve X Y 2 Dy Dx Maths Limits And Derivatives Meritnation Com
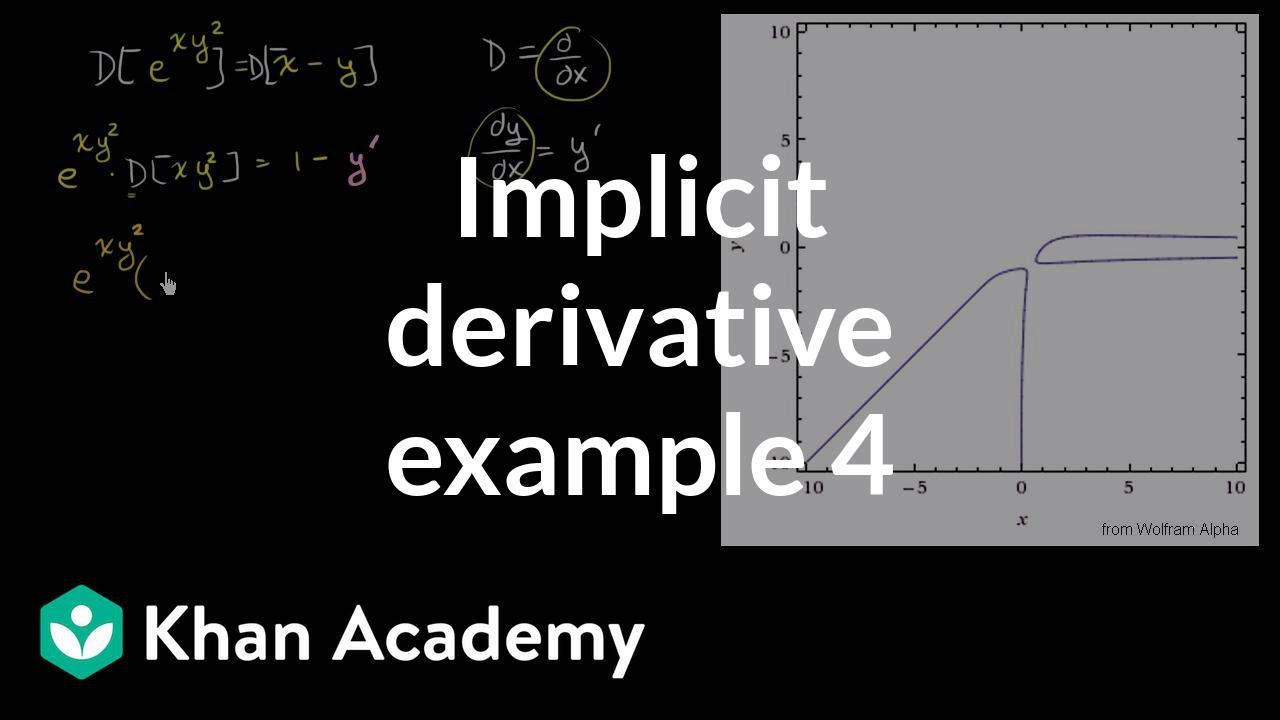


Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy



The Solution Of Dy Dx X 2 Y 2 2x 2 Is



Solve The Following Homogenous Differential Equation X2y 2xy2 Dx X3 3x2y Dy 0 Brainly In



Solved Solve The Equation Dy Dx Y Xy 3 1 Solve The Equation 1 Answer Transtutors



Engineering Mathematics Notes



The Solution Of The Differential Equation 1 Y X 2y Dx X



Ejercicios Propuestos Ecuaciones Diferenciales Primer Orden Pdf Differential Equations Equations



Y 2 X 2 Dy Dx Xy Dy Dx Youtube



Tan X Dy Dx 2x Tanx X 2 Y Y 0 And X 2 Maths Differential Equations Meritnation Com



Unit 03 Differential Equations Equations Trigonometric Functions
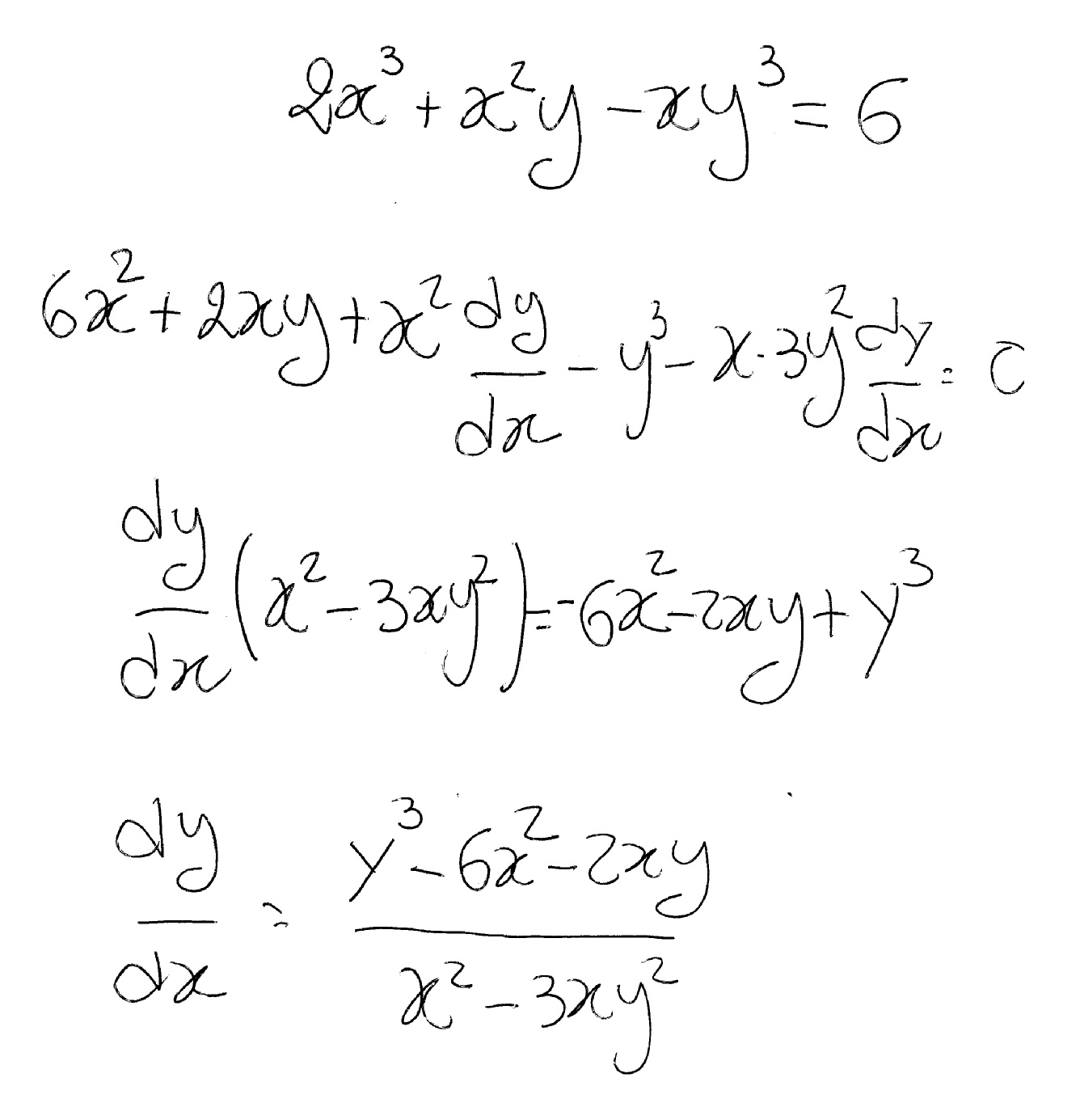


How Do You Find Dy Dx By Implicit Differentiation For 2x 3 X 2 Y Xy 3 6 Socratic



Misc 7 Show That General Solution Is X Y 1 A 1 X Y 2xy
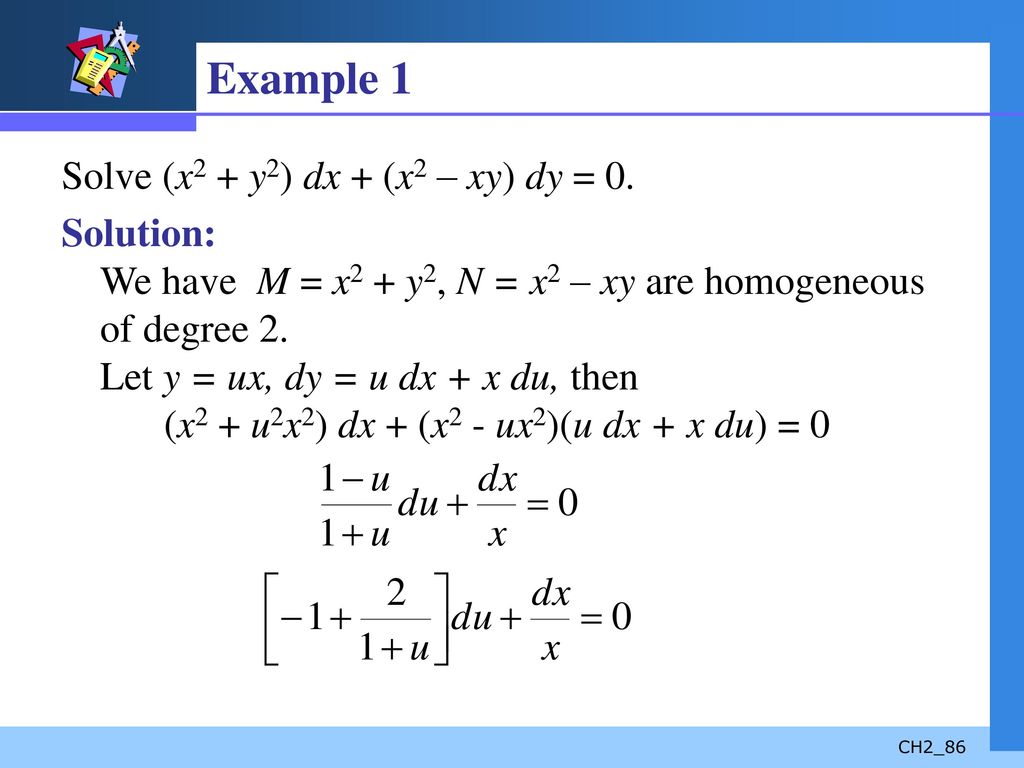


First Order Differential Equations Ppt Download
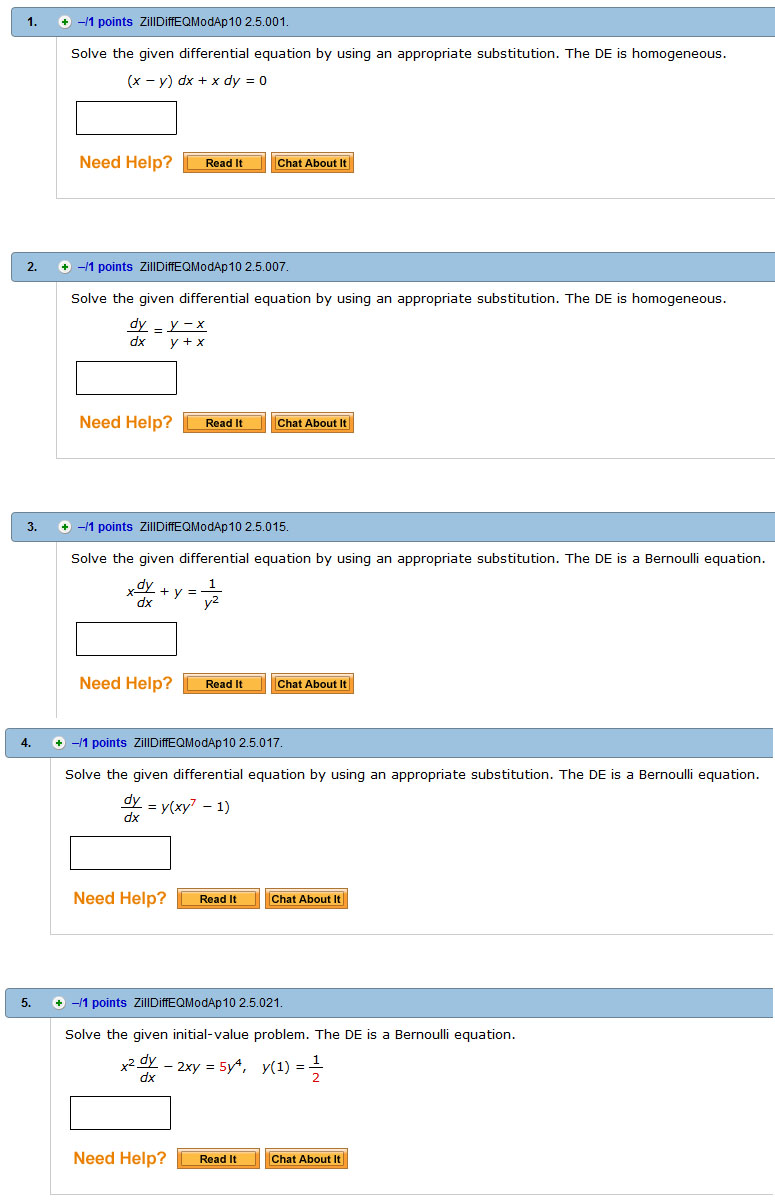


Solved Solve The Given Differential Equation By Using An Chegg Com


How To Solve This Differential Equation X 2 Y X 3dy Dx Y 4cosx Quora


What Is The Solution Of Y 2 Xy Dx X 2dy 0 Y 1 1 By Finding The Integrating Factor Of The Differential Equation Quora
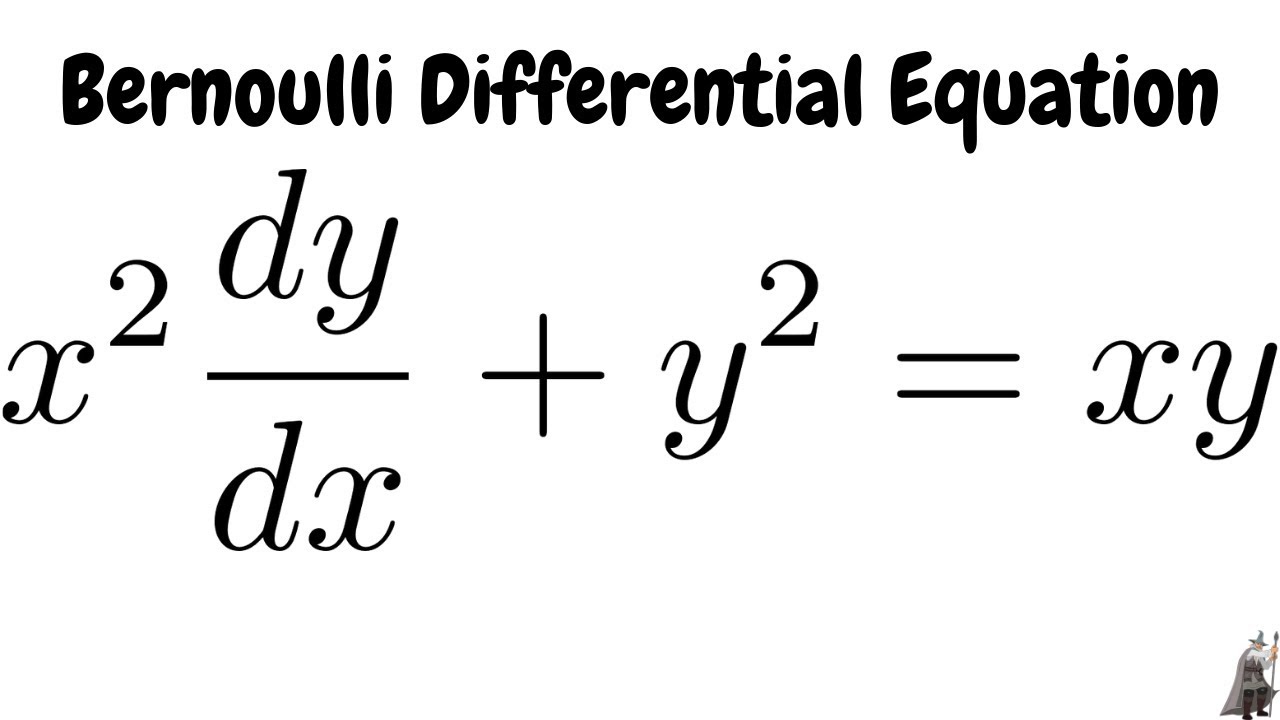


Solving The Bernoulli Differential Equation X 2 Dy Dx Y 2 Xy Youtube
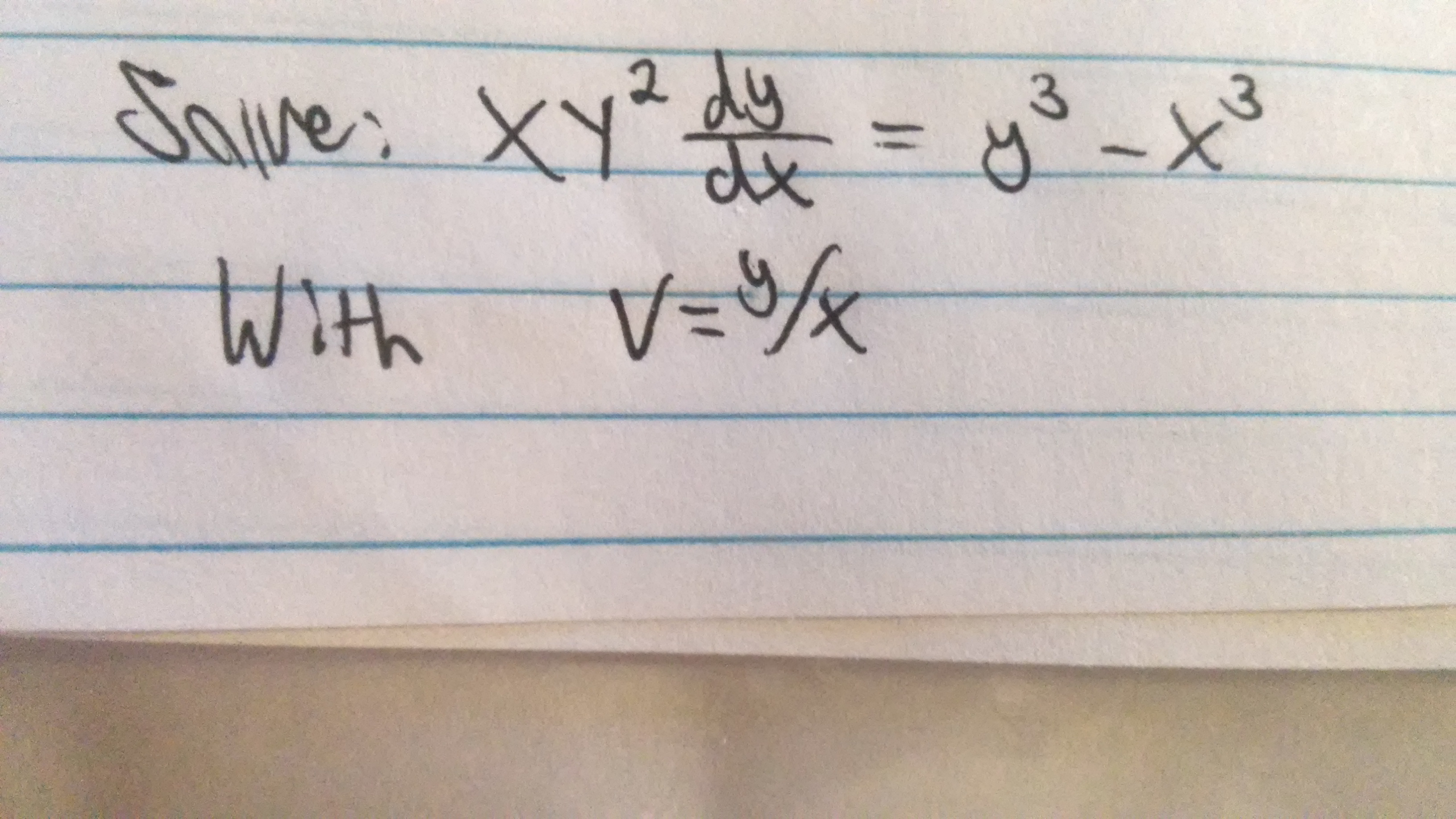


Solved Solve Xy 2 Dy Dx Y 3 X 3 With V Y X Differen Chegg Com


Solved Dy Dx Xy 2 1 X 2 2 Y 2 X 2 Dy 2xy Chegg Com



Xy 2 Dy Dx Y 3 X 3 Substitution V X Y



Engineering Mathematics Notes
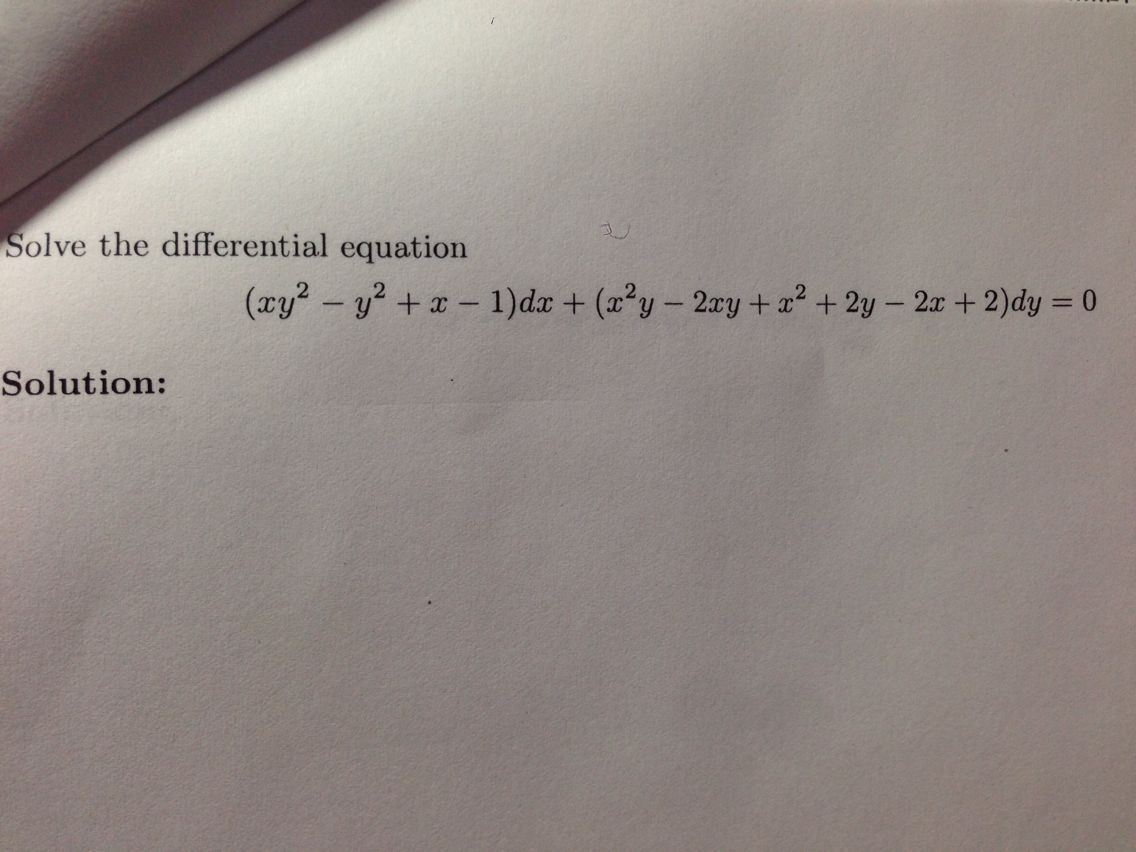


Solved Solve The Differential Equation Xy 2 Y 2 X Chegg Com



Ex 9 4 16 For Xy Dy Dx X 2 Y 2 Find Solution



Example 21 Find General Solution Ydx X 2y2 Dy 0



Engineering Mathematics Notes


Tinkutara Equation Editor Math Forum Question



Solving The Bernoulli Differential Equation X 2 Dy Dx Y 2 Xy Maths Exam Math Videos Differential Equations



Solve 2 Y 3 X Y Dy Dx 0 Given That Y 1 2


Solved Solve The Given Bernoulli Equation X Dy Dx Y 1 Y 2 Dy Dx Y E X Y 2 Dy Dx Y Xy 3 1 X Dy Dx 1 X Y Xy 2 X 2 Dy Dx Course Hero



Engineering Mathematics Notes



Solve The Differential Equation 2 Dy Dx Y X Square Y X Youtube
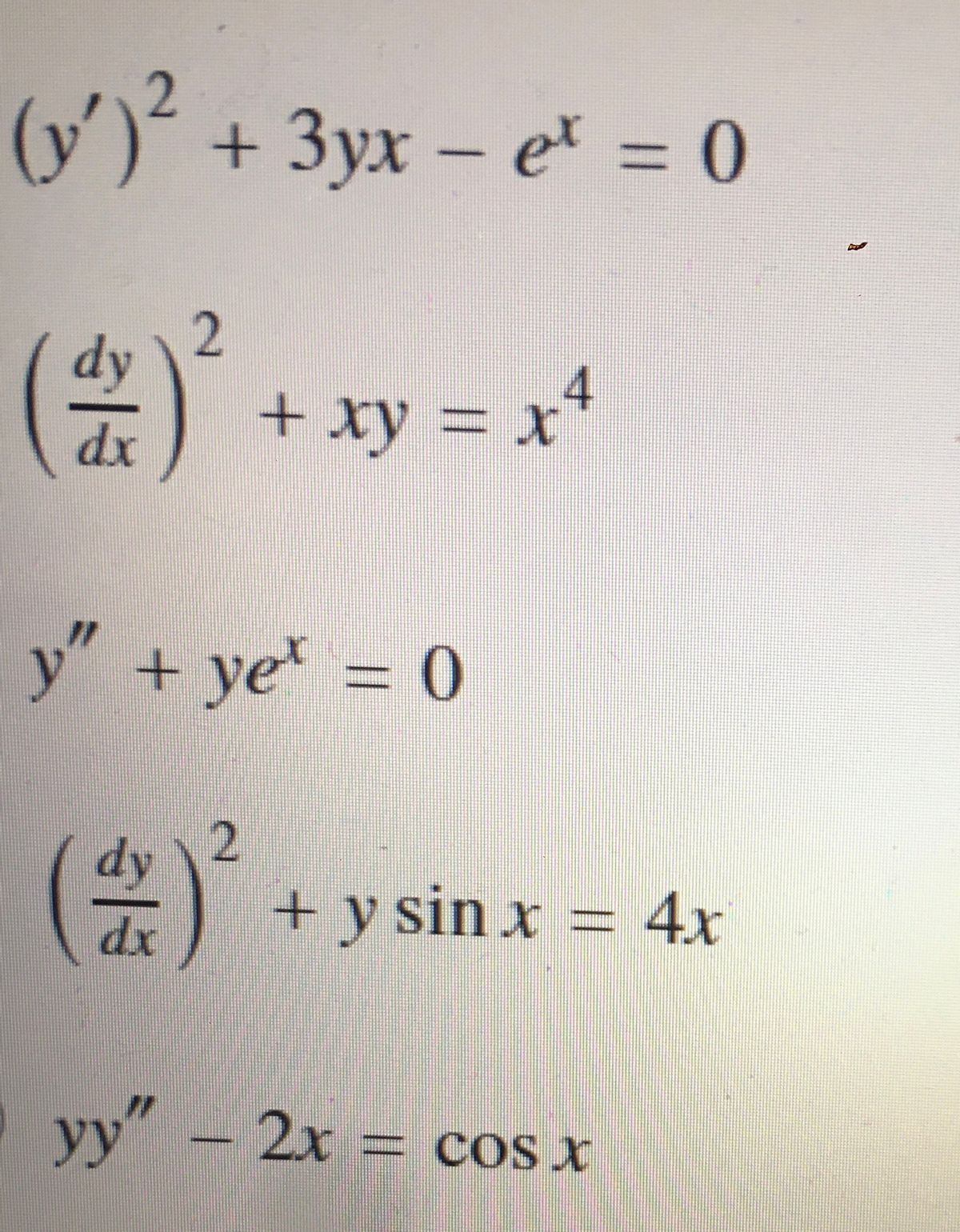


Answered 3yx E 0 3d Dy Xy X Dx Y Bartleby



Solved Solve The Differential Equation Dy Dx Xy 2 1 Chegg Com


How To Solve 3x Xy 2 Dx X 3 2y Dy 0 Quora



Worked Example Implicit Differentiation Video Khan Academy



Ex 9 5 12 Find Particular Solution X2 Dy Xy Y2 Dx 0



Solve Frac Dy Dx Y Tan X Y 3 Cos X Mathematics Stack Exchange



Solution Of Xy Dy Dx Y 3 E X 2 Is



Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf Free Download



Solution Of X Y 2 Dy Dx A 2 A Being A Constant Is Youtube



Hw 2 5 Solutions Differential Equations Equations


What Is The Solution Of Differential Equation D 2y Dx 2 2 Dy Dx Y 0 When X 0 Y 1 Dy Dx 2 Quora



Solve Y 2 2x 2y Dx 2x 3 Xy Dy 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Solve The Differential Equation X 2 Xy Dy X 2 Y 2 Dx



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿